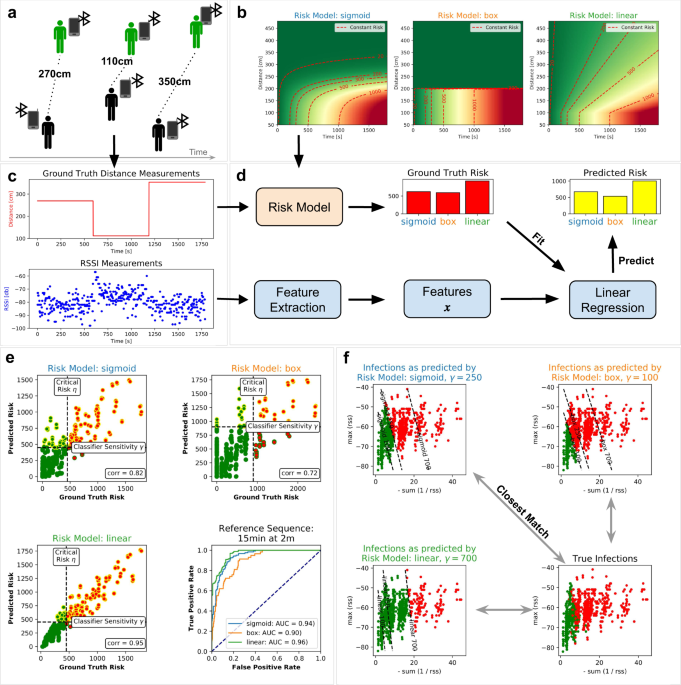
There are a number of studies related to Corona 19 using AI technology. The paper shared below is a study by Fraunhofer HHI published in Nature, which analyzes the figures measured from Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) using machine learning techniques to automatically identify risk groups among those who have contacted the confirmed patient. At this time, the false alarm is minimized by analyzing the contact distance and time.
Since most people have smartphones, and most of the latest smartphones support BLE, it can be considered a very practical study. It also appears to be an advantageous approach from the standpoint of strict privacy laws such as GDPR.
As a related story, ITU, an international standardization organization, formed a collaboration organization called Focus Group on “Artificial Intelligence for Health” in 2018 with WHO. It is chaired by Thomas Wiegand of Fraunhofer HHI, one of the well-known experts of video compression, and is also one of the authors of the paper I shared above.
The organization's goal is to develop a standard assessment methodology for AI-based methods applied in areas such as health checks, disease diagnosis, classification, and prescription. Given the characteristics of AI-based methods, it is judged to be meaningful in itself to consider risks that may arise in the medical field and to create guidelines by international consensus. Below is a link to this collaboration organization site.